With the continuous development of industrialization, sensors, as an indispensable component in the development of modern industry, are constantly innovating with the market needs. Today, Micro Sensor will introduce the widely-used digital pressure sensors to you today.
To begin with, we need to understand how digital sensors are different from the common sensors. Generally, the common sensors output analog signals, while digital sensors, as the name suggests, output digital signals. The difference between them is the communication protocols. Since we want to understand digital sensors, let's start with the communication protocol!
What is the Communication Protocol?
In simple terms, a communication protocol means in order to understand each other's meaning, both parties agree on some communication requirements in advance, such as data transmission format, synchronization method, transmission speed, transmission steps, error detection and correction methods, and control character definitions. etc., and it only exists in systems where signals are transmitted and received digitally.
How to Convert Analog Output to Digital Output
Digital and analog signals are actually just a way of signal transmission, with no essential difference, and they can be converted into each other. Common analog signals are: 0-100mV, 0-5V, 0-10V, 4-20mA, and common digital models are I²C, SPI, CAN, 485, etc. In order to more intuitively show the difference between digital signals and analog signals, we use this analog signal digitization process diagram to introduce it to you.
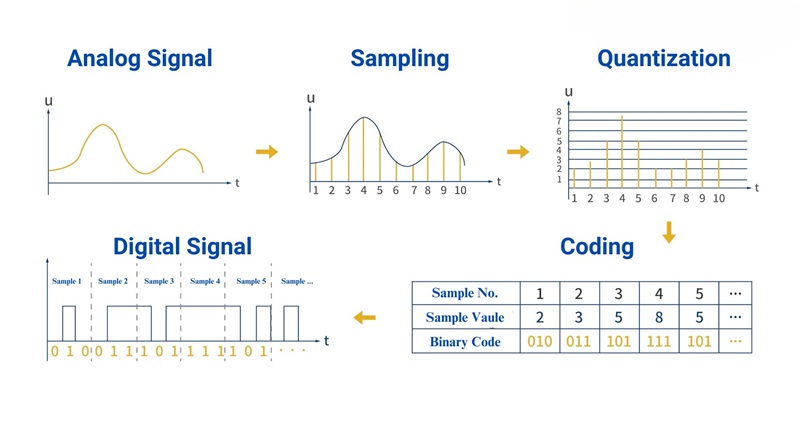
Two main steps of converting analog signals to digital signals are sampling and quantization. As can be seen from the figure, sampling is to collect the date on this continuous curve according to a certain time period and quantization is to obtain the specific value of each sampling point through comparison and directly generate the equal binary value. A more popular understanding: the analog signal is a line, and the digital signal is a point corresponding to a certain moment on the line.
But they all represent a certain characteristic of the event at a certain moment (such as pressure, gas concentration, sound information, etc.).
Advantages of Digital Output Pressure Sensors
• Strong Anti-Interference Ability
The maximum signal of the analog sensor is about tens of millivolts, and it is easy to be interfered in the process of weak signal transmission in the cable. The output signal of the digital sensor only has high and low levels, and the high level can generally reach 3 to 4V, and the anti-interference ability is much larger than that of the analog signal by a million times.
• Convenient
The output signal of the digital sensor is in the form of binary code, which is convenient for storing, processing and exchanging digital signals with systems such as computers, and is also convenient for customers to carry out network management, automation and intelligent maintenance.
• Lower Power Consumption
The digital sensor adopts time-division multiplexing, which does not require a large-scale filter and can be implemented by large-scale and ultra-large-scale integrated circuits, so it is smaller in size and lower in power consumption.
Micro Sensor's Digital Pressure Transmitters
Micro Sensor offers a series of digital output pressure transmitters as below:
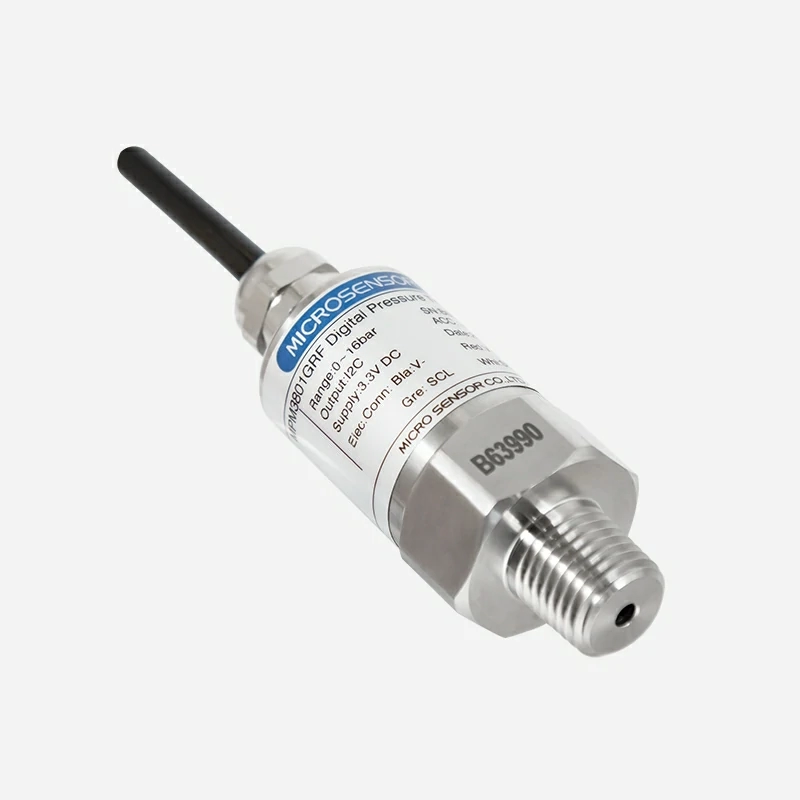
MPM3801A pressure transmitter outputs digital IIC / SPI. It includes two versions: Type I and Type II, and is widely used in process control and pressure and liquid level measurement in the petrochemical industry, Internet of Things, electric power, aviation, aerospace, textile, building materials, hydrogeology, etc.
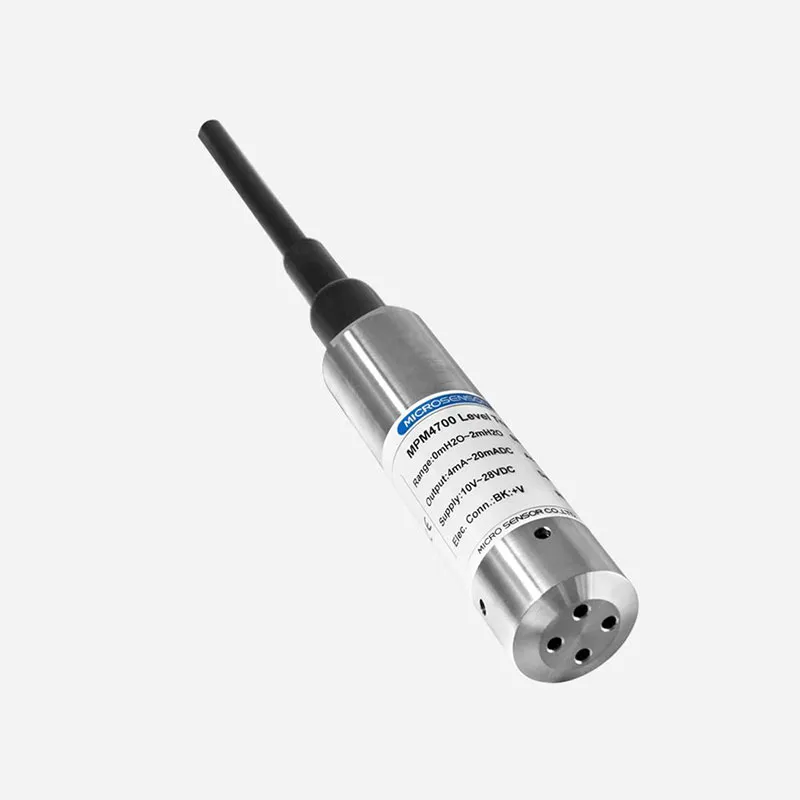
MPM4700 level transmitter can output analog 4-20mA DC and digital RS485 signal. It has typical ±0.1%FS high accuracy, owns RoHS certification, intrinsic safe version, and obtained marine ship-use type use, widely used for industrial field instead of normal 2-wire 4mA~20mA DC analog output transmitter.
Micro Sensor has a professional R&D team to offer customized product solutions. Feel free to contact us for any needs.






























 Copyright © 2026 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD
Copyright © 2026 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD