
Hello, everyone, Dr. Mike's class has started again! The popular science of pressure sensors will usher in the final chapter of this issue!
Previously, we have respectively popularized the nonlinearity, repeatability, and hysteresis of the pressure sensor which all determines the accuracy of the pressure sensor. Today, Dr. Mike will talk about the accuracy of the pressure sensor!
What is the Accuracy of the Pressure Sensor?
Accuracy is a value that combines the effect of linearity, hysteresis, repeatability, and thermal drift, which is divided into basic accuracy and full accuracy. Basic accuracy refers to the value measured under a certain reference condition (generally 25°C), excluding the temperature effect.
Full accuracy is a value measured over a specified temperature range, including the temperature effect. Each sensor will be attached with a label marked the non-linearity, hysteresis, repeatability and other parameters before out of factory.
How is the Accuracy Calculated?
So how should the important value - accuracy, be calculated?
Formula 1: (Basic accuracy calculation)
Accuracy equal to the root value of the sum of non-linearity squared, Hysteresis squared, and repeatablility squared.
Steady-state performance of pressure sensors (basic error, excluding temperature effect), or only the accuracy class. The actual performance should meet the corresponding level or higher level requirements.
The relationship between the accuracy class and performance is specified in the following table.
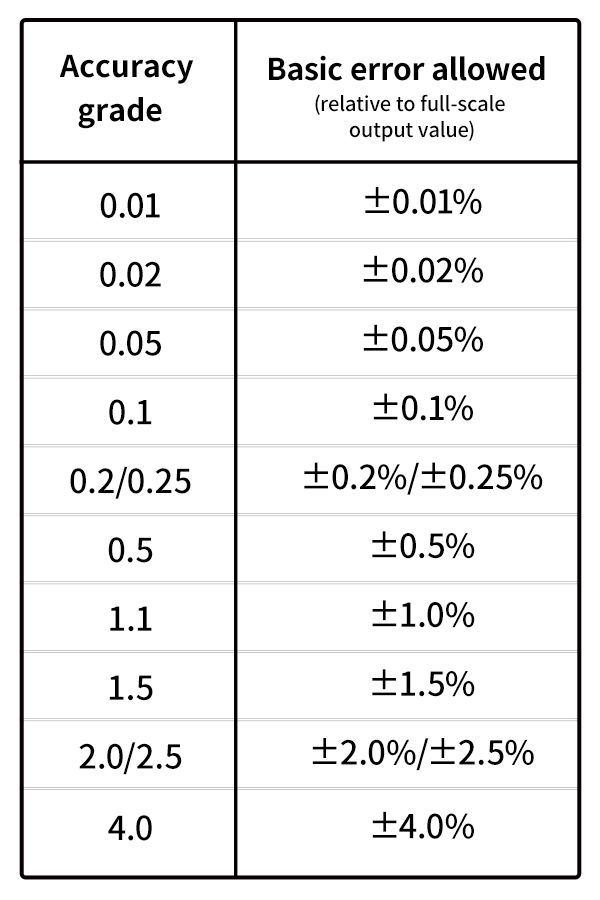
Note: values in parentheses are not recommended.
(Take MPM281 as an example, nonlinearity: ±0.15%FS (typical), repeatability: ±0.05%FS (typical), hysteresis: ±0.05%FS (typical), wherein, basic error= 0.16%FS, accuracy class is > 0.2)
From General Specification for the Piezoresistive Pressure Transducer "SJ/T 10429-93"
Formula 2: (full accuracy calculation)
Accuracy equal to the root value of the sum of NL squared, RP squared, HY squared and TCP/Tcps divisor squared
Also known as full accuracy error (comprehensive error)
NL: nonlinearity (%Span)
HY: hysteresis (%Span)
RP: repeatability (%Span)
TCZ: zero thermal error (%Span)
Tcsp: full-scale thermal error (%Span)
These two calculation methods are measured according to international standards, and are also what Micro Sensor often used, so the precision results are reliable. There are many factors that affect the accuracy of the pressure sensor, and the main parameters such as nonlinearity, hysteresis, and repeatability have many ways to calculate as well. Therefore, the calculation results will be slightly different, which is quite normal.
How Does Micro Sensor Improve the Sensor Accuracy?
1-Auto bonding
2- Laser welding temperature compensation board
3-Laser trimming
Micro Sensor Pressure Sensor Family
After these optimization steps, Micro Sensor developed sensors such as MPM281 high-stability pressure sensor and MPM280 Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor with high-stability and high-precision, with excellent performance, high stability and accurate measurement. These small pressure sensors have huge energy and play an important role in all kinds of industrial equipments.

Well, that's all for today, and if you want to know some new, please tell Dr. Mike by the comment area! See you next time!






























 Copyright © 2025 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD
Copyright © 2025 MICRO SENSOR CO., LTD



